BIM-IoT data integration at Hospital del Mar
Date: 07/05/2018
Language: English
Origin: Pinearq
Web: see here
Author: Abraham Jiménez
Spanish version: see here
For some years now, the consolidation of BIM (Building Information Modeling) in architecture, engineering and construction is generating a debate on the proposition that BIM data captured during the project’s lifecycle could improve the efficiency of managing built constructions. Based on our professional experience, at Pinearq we are convinced that integrating data created on BIM into management processes supported by IoT (Internet of Things) is only a matter of time, and so we are committed to contributing to research focused on speeding up this process in healthcare infrastructures. This article proposes, first, a series of reflections on the implications of integrating BIM data into the management processes of buildings; and second, presents an ongoing project led by Pinearq and Hospital del Mar aimed at increasing efficiency in the management of a hospital building by linking up BIM databases with IoT networks.
The integration of BIM data into the management of healthcare infrastructures
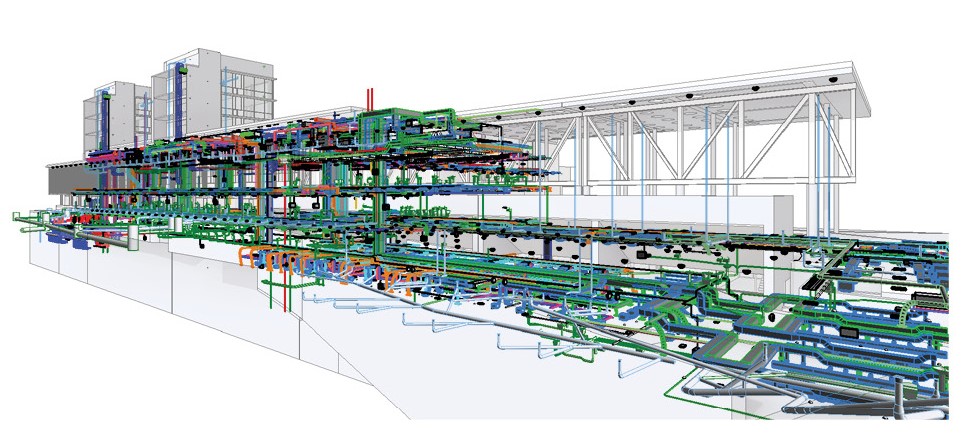
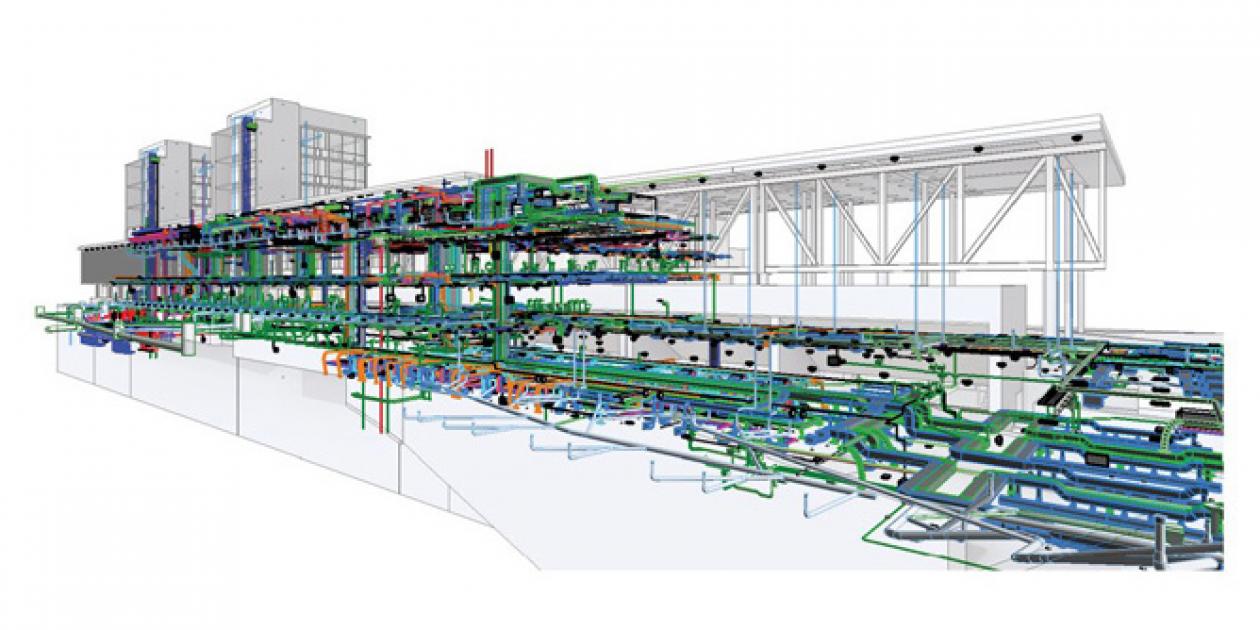
Image 1. BIM Model of Hospital del Mar Building Enlargement Phase 1
BIM represents a building as a database of coordinated information, consistent and computable in the construction. To work in BIM is to work collaboratively through a common interconnected platform to include all stakeholders in a project. As BIM becomes consolidated among architects, engineers and builders, the need increases for greater effectiveness in managing buildings. According to a 2002 report by the US National Institute of Standards and Technology, the costs incurred due to the inadequate interoperability of data in the Facility Management (FM) industry amounted to US$ 15.8 billion.
The report mentions that more than 65% of this cost is borne by the owners of the facilities. Interestingly, almost 85% of this expenditure, namely around US$ 9 billion, will be made during the maintenance and conservation phases of the facility’s lifecycle. Taking these trends into account, it is reasonable to ask ourselves about the benefits of incorporating the information contained in BIM into the management and maintenance process of buildings. Creating information models in BIM has the potential of generating a radical change in the way buildings and their installations are managed. Growing numbers of stakeholders around the world, especially in North America, are recognizing this fact.
For the administrators of healthcare infrastructures, BIM’s potential consists of providing a central information depot for their operational tasks that can to a great extent speed up their problem-solving process. Moreover, as the information modelling for buildings continues to develop and its integration into the infrastructure management processes is researched, new possibilities are cropping up for interacting with technologies focused on capturing data on the operation and performance of buildings. With the arrival of smart-buildings technology, increasing numbers of buildings are being equipped with smart automation systems, which means the use of several types of sensors for obtaining large quantities of data as an aid in assessing the building’s performance.
These can be used for supporting any decisions taken on the running of facilities and equipment maintenance. These smart systems open up the possibility of integrating real-time data compiled and accumulated by sensors together with the spatial and technical information extracted from a BIM model. Such an integration can be advantageous in monitoring the performance of systems and construction processes and in assessing the decisions relating to the administration and operations of the infrastructures.
Benefits and challenges of BIM-IoT data integration
The IoT has consolidated home automation as a flourishing market, but which are the possibilities when applied to non-residential, technically highly complex buildings? Information modelling for construction has appended never-before-seen vision and connectivity for all types of buildings; even so, when complemented with IoT, the capabilities of future BIM systems will vastly improve daily operations and the management of the facilities. By linking up BIM + IoT, building automation, which encompasses the comprehensive automation of high-tech buildings, will become the next major development in building management and will open up new possibilities. Sensors are quickly evolving towards increasingly autonomous wireless technologies. Nowadays wireless sensor networks are capable of self-configuring and networking, making them an attractive solution for several FM applications.
This technological evolution, which is known as the “Internet of Things” (IoT), is one of the pillars of the digital evolution we are experiencing and is already being widely used for a variety of purposes, including environmental monitoring, managing assets, maintaining facilities, a building’s security and several other applications. In recent years a multiplicity of studies have been conducted to boost the use of BIM in managing facilities in the phases following construction.
These include the linking of the BIM model with smart detection technology or building automation systems. Understanding the challenges and the potential of BIM’s aggregate value for IoT systems is crucial in this initial stage. The benefits of using BIM databases for managing and maintaining buildings include, among others:
- Improving current information-delivery processes; improving the precision of data for designing and managing infrastructures.
- Increasing the efficiency, in terms of speed, of executing work orders to access data and locate interventions. This value is derived from BIM’s ability to provide a data-rich visual and integrated environment.
- Faster problem solving and efficient management of facilities through information shared among the facility administrators and all necessary contractors within the industries of architecture, engineering, construction and management.
- Better simulation during updating and overhaul projects through an exhaustive design analysis on the BIM platform.
- Cost control and reduced overheads by predicting a building’s performance throughout the facility’s lifecycle, analyzing data and establishing trends, allowing for a better and more precise budget assigned to future maintenance.
The introduction of BIM in building management depends to a large extent on obtaining relevant information from BIM to perform significant actions with it, but this does not mean that such integration is a direct route. Several issues must first be resolved, among them improving the interoperability of the data and software used in both industries; adapting the BIM model to the needs of its managers; and the cultural change involved in introducing a new technology in the management of buildings.
Despite these obstacles, the functionalities provided by BIM for FM constitute a major stimulus in driving the integration of these two worlds. Among the most relevant ones are those associated with the nature of BIM visualization, which provides precise geometric data that had hitherto not been possible, allowing for the analysis of proposals for a building’s construction, simulation and performance.
Other important applications of BIM-IoT integration are space management as well as energy control and supervision. It is expected that adopting BIM data will provide ways of managing the knowledge on operations within the building that can be used in future designs. This centrality of information provides gains in efficiency that are not possible with the current processes and technologies used by the FM team.
Para poder escribir un comentario debe iniciar sesión o darse de alta en el portal.